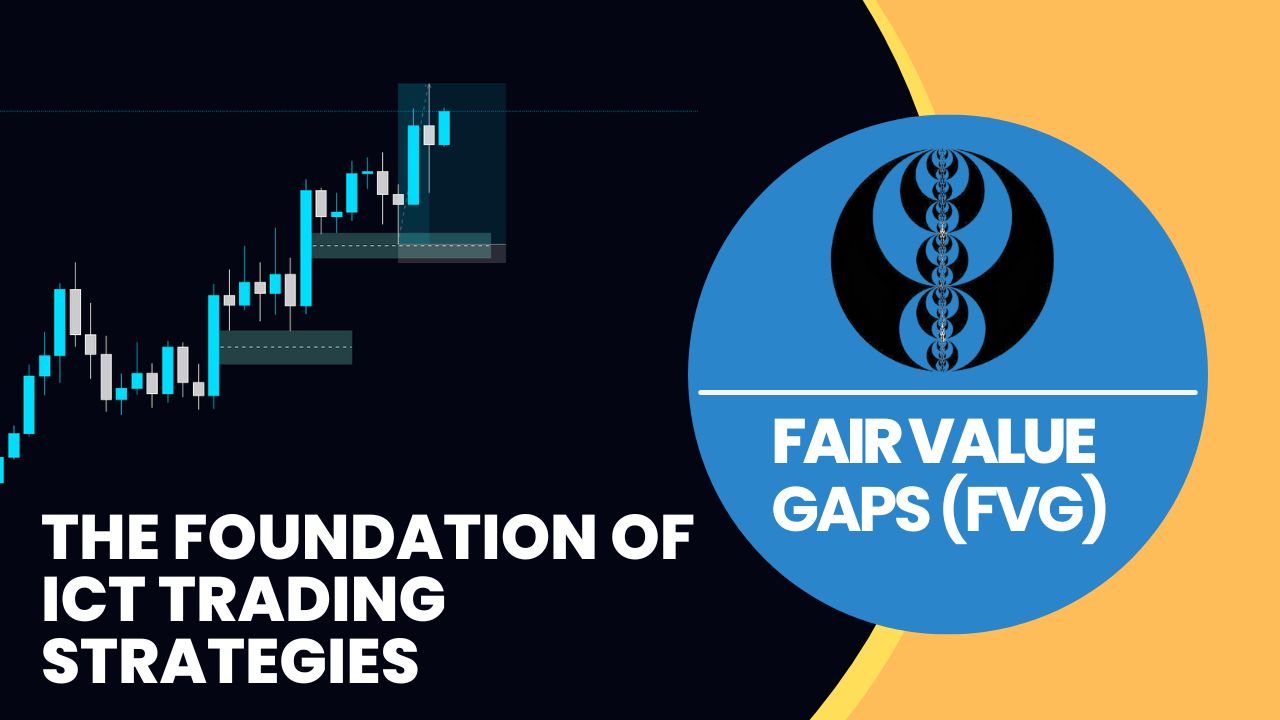
Decoding Fair Value Gaps (FVG) in ICT Trading Strategies
The market presents many gaps in what we call fair value gaps. ‘ Each of these fair value gaps represents an insight into the impossibility of the market, which shows that a particular price action skips certain levels. This is left with outstanding areas that institutional traders usually return to.
This gives you an overview of what FVG means what they are, why they are important, and how to use them for better results in your trading plan. By the end of this guide, you should already have a clear idea of spotting and trading FVGs for better performance.
What Is the Fair Value Gap FVG?
A fair value gap is the space between the high and low of candles from the closing point of one candle to the opening point of the next candle that goes unfilled by price action. This indicates less liquidity in the market due to the fast-moving price.
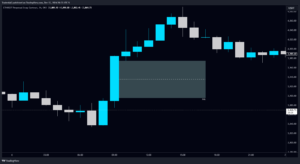
Features of FVGs
- Occurs in Strong Trends: FVGs are more likely to happen when impulsive moves occur.
- Indicates Market Imbalance: Then price delivery’s inefficiency will be signified through the gap.
- Revisited by Price: Retracement often occurs in these gaps, which is needed to align the order flow.
Why FVGs matter?
- Reveal Smart Money Activity: Smart Money Institutions frequently fail to leave these gaps when executing large orders.
- Entry Opportunities: Retracements to FVG may act as optimal entry points.
- Market Trend Identification: FVGs may affirm the strength of a trend or signal a turning point.
Identify FVGs on the Chart:
- Analyze Impulsive Moves: Observe to see whether prices shift swiftly over a considerable range.
- Spot the Gap: This is where the high of one candle is compared to the low of the next; it is the gap.
- Mark the FVG: Highlight that gap on your chart for future reference.
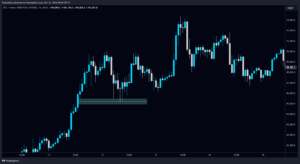
Real-World Scenario:
Let us assume an FVG revolves within a bullish atmosphere, forming that gap at $1,800 for an ETH during a very sharp rally. The price action is then able to retrace this level before heading back to $1,850 at a later time frame. A trader familiar with FVG would likely open a long trade from $1,800, with a stop-loss just below $1,790, enabling risk management practices.
What’s Next?
Fairtrade gaps are the prime source for trading in ICT; however, they are even better when related to other concepts such as liquidity and order blocks. The next post will be about liquidity zones and how they are relative to FVGs in creating more serious trade setups.
Call to Action
Continue following this blog series on ICT trading strategies by bookmarking our site, The Traders Floor. Join our Discord and follow us on Twitter for live trade ideas and updates!